Data Governance Best Practices: Ensuring Quality, Security, and Compliance
Effective data governance ensures high-quality, secure, and compliant data management. Learn how to define roles, streamline access, implement security measures, and conduct audits to maintain data integrity. Explore best practices to optimize governance frameworks and drive business success.
Effective data governance ensures data remains accurate, secure, and compliant throughout its lifecycle. Organizations that implement well-defined policies for data quality, privacy, and security can mitigate risks and enhance decision-making. Data stewardship plays a critical role in maintaining standards, while metadata management structures and catalogs information for better accessibility and control.
Without a structured approach, businesses face challenges with inconsistent data, regulatory non-compliance, and operational inefficiencies. Implementing best practices in governance establishes trust in data assets and aligns strategic objectives with regulatory requirements.
Setting Up a Data Governance Framework
Defining the Key Components of a Data Governance Framework
Building a structured data governance framework requires clearly defined components that ensure consistent policies, roles, and responsibilities. A well-formed framework typically includes:
- Governance Policies and Standards:
- Roles and Responsibilities:
- Data Classification Strategy:
- Process and Workflow Design:
- Technology and Tools:
Establish uniform rules for data management, usage, security, and compliance.
Assign clear duties to data stewards, data owners, and governance committees to oversee data quality and adherence.
Define categories such as confidential, public, and internal data to apply appropriate controls.
Map out how data flows through its lifecycle, ensuring consistency in data handling.
Integrate data management platforms, metadata repositories, and automated compliance enforcement mechanisms.
Each of these components must align with organizational objectives and regulatory requirements. Clear documentation ensures that governance policies remain actionable and enforceable.
Ensuring Data Ownership and Accountability
Data governance operates effectively when ownership and accountability are clearly assigned. Without defined ownership, organizations struggle with inconsistent data handling, security risks, and compliance violations.
- Data Owners:
- Data Stewards:
- Governance Committees:
Designated individuals or teams responsible for data integrity, security, and compliance within their domain.
Operational roles that ensure data policies are adhered to and provide oversight on data usage.
Cross-functional teams that establish policies, resolve disputes, and drive governance initiatives.
Data owners make strategic decisions, while data stewards handle day-to-day governance tasks. Governance committees ensure alignment with policies and regulatory mandates. Together, these roles create an accountability framework that sustains data integrity and compliance across the organization.
Pro Tip – Establish clear escalation paths for data-related issues to enhance data ownership and accountability. Define who to contact when data discrepancies arise and ensure that resolution timelines are documented. This prevents delays, minimizes risks, and promotes a culture of responsibility within the organization.
Strategies for Robust Data Security
Organizations handle vast amounts of sensitive information, making data security a top priority. Preventing breaches and blocking unauthorized access requires a multi-faceted approach. Encryption, access controls, and vulnerability assessments form the foundation of a strong security strategy.
Encryption: Protecting Data at Rest and in Transit
Encryption ensures that data remains unreadable to unauthorized users. Advanced encryption standards (AES) with 256-bit keys provide strong security for stored data. Transport Layer Security (TLS) encrypts information in transit, safeguarding communications between applications, databases, and users.
- End-to-end encryption secures data from sender to receiver, preventing exposure during transmission.
- Transparent data encryption (TDE) protects databases by encrypting files at the storage level.
- Public key infrastructure (PKI) enhances authentication and confidentiality through digital certificates.
Access Controls: Restricting Unauthorized Entry
Limiting data access minimizes risk. Role-based access control (RBAC) assigns permissions based on job responsibilities, restricting exposure to necessary information only. Attribute-based access control (ABAC) refines permissions further by incorporating contextual elements such as location and device type.
- Multi-factor authentication (MFA) requires users to verify identity through multiple credentials before gaining access.
- The least privilege principle ensures employees access only the data and systems essential to their role.
- Privileged access management (PAM) secures administrative accounts by enforcing strict usage policies and session monitoring.
Vulnerability Assessments: Identifying Weak Points
Regular assessments expose security flaws before attackers exploit them. Automated vulnerability scanning tools detect misconfigurations and outdated software, reducing attack surfaces. Penetration testing simulates cyberattacks to evaluate system resilience.
- Patch management ensures timely updates to eliminate vulnerabilities in operating systems and applications.
- Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems detect unusual activity by analyzing security logs in real-time.
- Zero Trust Architecture eliminates implicit trust for devices and users, enforcing continuous authentication.
Strong encryption, strict access controls, and proactive vulnerability assessments build a resilient data security framework. Organizations that implement these measures reduce exposure to cyber threats while maintaining compliance with regulatory standards.
Pro Tip- Regularly update and rotate encryption keys to strengthen security. Implement key management solutions (KMS) to automate key generation, distribution, and expiration, reducing the risk of compromised encryption.
Emphasizing Data Lifecycle Management
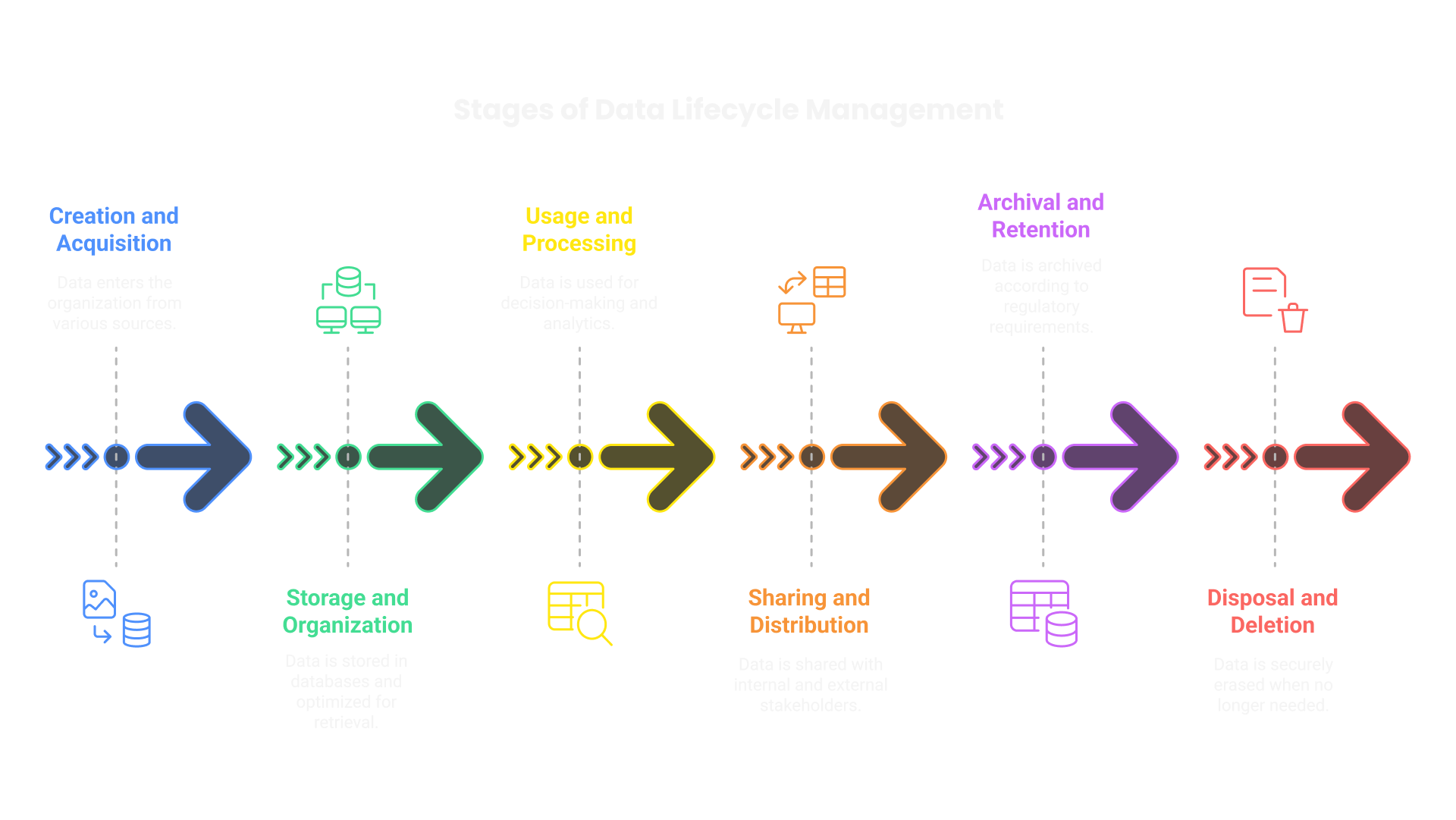
Ensuring Data Relevance and Proper Retirement
Data loses value over time. Without governance, outdated records create inefficiencies and compliance risks. Organizations must establish procedures to maintain relevance and retire obsolete data appropriately.
- Data Classification:
- Regular Audits:
- Retention Policies:
- Secure Data Disposal:
Assigning data categories helps determine retention periods and access levels. Critical, sensitive, and temporary data require distinct handling policies.
Periodically reviewing datasets identifies redundancies, inconsistencies, and outdated records. Automated audits streamline this process.
Industry standards and regulations dictate how long data must be stored. Defining clear retention policies prevents excessive accumulation.
Overwriting techniques, cryptographic erasure, and physical destruction ensure permanent data removal. Compliance with frameworks like GDPR and HIPAA necessitates rigorous disposal methods.
Effective data lifecycle management aligns governance with business needs. Whether optimizing storage, enforcing access controls, or ensuring regulatory adherence, every stage plays a role in maximizing data value while minimizing risks.
Managing Data Storage and Operations
Organizations generate vast amounts of data every day, requiring efficient storage solutions and well-structured operational strategies. Managing data storage and operations involves selecting the right storage infrastructure, ensuring scalability, and optimizing performance for high availability and reliability.
Choosing the Right Data Storage Solutions
Storage solutions must support performance demands while aligning with organizational goals. Structured and unstructured data require different storage strategies, and hybrid models often provide the best balance of cost, accessibility, and performance.
- On-Premises Storage:
- Cloud Storage:
- Hybrid Storage:
Offers full control over data but requires significant maintenance and upfront costs.
Provides scalability and reduces infrastructure overhead, with options like Amazon S3, Google Cloud Storage, and Microsoft Azure Blob Storage.
Combines on-premises and cloud-based solutions to balance security, compliance, and scalability.
Cloud providers offer tiered storage options, allowing organizations to classify data based on frequency of access and retention policies. Cold storage options such as AWS Glacier significantly reduce costs for infrequently accessed data.
Scalability and Performance Optimization
As data volumes grow, storage solutions must scale efficiently. Horizontal scaling-adding more storage nodes ensures that storage infrastructure can expand without downtime. Object storage models, such as those used in cloud environments, support massive scalability with minimal performance degradation.
Optimizing performance involves:
- Using data partitioning to distribute workloads across multiple storage units.
- Implementing caching strategies with in-memory solutions like Redis or Memcached for faster data retrieval.
- Leveraging compression and deduplication to reduce storage footprint while maintaining data integrity.
- Automating tiered storage policies to move data between high-performance and archival storage based on usage patterns.
Operational Best Practices for Data Storage
Efficient data storage operations rely on systematic processes that ensure data integrity, availability, and recoverability.
- Regular Backups:
- Disaster Recovery Plans:
- Storage Access Controls:
- Monitoring and Alerts:
Implement incremental and full backups to minimize data loss risks.
Establish geographically redundant storage and failover mechanisms for business continuity.
Define access policies to restrict unauthorized modifications and data breaches.
Utilize automated monitoring tools to detect abnormal storage usage patterns and prevent system failures.
Balancing Cost and Performance with Cloud-native Solutions
Enterprises moving to cloud-native infrastructures benefit from elasticity and cost-effectiveness. Services like AWS Auto Scaling and Kubernetes persistent volumes adjust resource allocation dynamically based on real-time demand.
To optimize cost-effectiveness:
- Utilize auto-tiering to reallocate old data to lower-cost storage.
- Adopt serverless storage options like AWS Lambda and Google Cloud Functions for event-driven data operations.
- Monitor usage patterns with cost analytics tools to prevent overspending on underutilized storage.
Handling data storage and operations requires a strategic approach that integrates scalability, security, and cost-efficiency. Well-defined storage policies and proactive infrastructure management drive sustainable data governance.
Pro Tip – Regularly audit storage usage and automate lifecycle policies to prevent data sprawl. Implement storage analytics tools to track data growth, identify redundant files, and optimize costs by shifting infrequently accessed data to lower-cost storage tiers.
Establishing Data Ownership and Accountability
Defining Clear Responsibilities for Data Assets
Assigning ownership to specific individuals or teams ensures control over data accuracy, security, and compliance. Without defined accountability, data governance efforts weaken, leading to inconsistencies and security gaps. Organizations must designate data owners and stewards, outlining their responsibilities explicitly.
- Data Owners:
- Data Stewards:
- Executive Sponsors:
Individuals responsible for the integrity and governance of a specific dataset. They establish data policies, approve access requests, and ensure regulatory compliance.
Professionals tasked with implementing governance policies, maintaining data quality, and facilitating data usage in alignment with business needs.
Senior leaders who provide strategic oversight, ensuring that data governance aligns with business objectives.
Establishing a structured hierarchy of ownership prevents decision-making bottlenecks and enhances operational efficiency. By integrating clear roles into governance frameworks, businesses maintain oversight while empowering teams to act swiftly when issues arise.
The Impact of Ownership on Data Quality and Compliance
Data ownership directly influences data accuracy, consistency, and adherence to legal requirements. When responsibilities remain undefined, redundant, outdated, or incorrect data proliferates, disrupting decision-making processes.
- Improved Data Accuracy:
- Regulatory Compliance:
- Efficient Issue Resolution:
Owners ensure consistency by implementing validation rules, resolving inconsistencies, and enforcing data entry standards.
Ownership structures simplify adherence to GDPR, CCPA, and other regulations by defining who is accountable for privacy measures and retention policies.
A designated owner streamlines data issue resolution by reducing ambiguities over who should address quality or security concerns.
Organizations integrating data accountability into governance models reduce operational risks and strengthen compliance efforts. Without ownership, data-related decisions become fragmented, leading to inefficiencies and vulnerabilities.
Pro Tip – Implement a Data Accountability Matrix (RACI model) to clearly define who is Responsible, Accountable, Consulted, and Informed for each data asset. This prevents overlap in responsibilities, ensures compliance, and accelerates decision-making in governance processes.
Streamlining Data Access and Permissions
Defining Access Controls to Prevent Misuse
Unauthorized data access creates security risks and compliance violations. A structured access control model defines who can view, modify, and share data within an organization. Role-based access control (RBAC) assigns permissions based on user roles, ensuring employees only access data relevant to their functions. Attribute-based access control (ABAC) enhances this by incorporating user attributes such as department, location, and experience level.
Implementing least privilege principles minimizes exposure. Users receive only the minimum access necessary to complete their tasks, reducing the attack surface for malicious activity. Regular access reviews remove outdated permissions, preventing former employees or contractors from retaining unnecessary access.
- RBAC: Assigns permissions based on predefined roles.
- ABAC: Uses dynamic attributes to refine access control.
- Least privilege: Grants minimal access necessary for tasks.
- Access reviews: Periodically reassesses permissions to prevent overexposure.
Balancing Availability and Protection
Data access policies must facilitate efficiency while maintaining security. Overly restrictive policies hinder productivity, while excessive accessibility increases risks. Striking the right balance involves segmenting data based on sensitivity levels. Public data remains widely accessible, while highly confidential information requires multi-factor authentication and encryption.
Just-in-time (JIT) access further refines this balance. Employees receive temporary access to sensitive information only when necessary, automatically revoking permissions after a set duration. This approach limits prolonged exposure while maintaining operational agility.
- Data classification:
- Multi-factor authentication (MFA):
- Just-in-time access (JIT):
Categorizes data based on sensitivity.
Adds extra security layers for critical data.
Enables temporary permissions for time-sensitive tasks.
Automating Permission Management
Manual access management slows down workflows and increases the risk of human error. Automation solutions streamline permission assignment, enforce compliance, and enhance security monitoring. Identity and access management (IAM) platforms integrate with enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems to synchronize user roles with existing corporate structures.
Automated provisioning and de-provisioning prevent access discrepancies. When an employee changes roles or leaves the organization, permissions adjust or deactivate instantly. Continuous monitoring with AI-driven anomaly detection identifies unusual access patterns, triggering alerts for potential breaches.
- IAM integration:
- Automated provisioning:
- Anomaly detection:
Connects access management with business operations.
Grants appropriate permissions during employee onboarding.
Flags irregular access patterns for review.
Pro Tip – Use Self-Service Access Requests with Approval Workflows to enhance efficiency while maintaining security. This allows employees to request access through an automated system, with approvals routed to data owners, ensuring compliance and reducing IT workload.
Proactive Data Auditing and Monitoring
Strengthening Governance Through Regular Audits
Consistent auditing identifies compliance gaps, security vulnerabilities, and inconsistencies in data processes. Organizations that conduct structured audits gain precise insights into data integrity, regulatory adherence, and operational efficiency. Establishing a systematic review process ensures data policies remain aligned with evolving business needs and legal obligations.
- Compliance Audits:
- Quality Audits:
- Security Audits:
- Process Audits:
Validate adherence to regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, and CCPA by systematically reviewing data usage and protection measures.
Assess the accuracy, consistency, and completeness of datasets, preventing flawed insights and operational inefficiencies.
Identify unauthorized access, unusual activity, and potential breaches to fortify defensive strategies.
Evaluate data handling workflows to pinpoint inefficiencies and inconsistencies in governance execution.
Advanced Monitoring Tools and Techniques
Automated monitoring tools enable real-time tracking of data activity, ensuring prompt detection of anomalies and policy violations. Leveraging AI-driven solutions enhances predictive capabilities, allowing proactive mitigation of risks before they escalate into major issues.
- Data Loss Prevention (DLP) Systems:
- SIEM (Security Information and Event Management):
- Data Anomaly Detection:
- End-to-End Data Lineage Tracking:
Monitor sensitive data movement, blocking unauthorized transfers and mitigating exposure risks.
Aggregate log data across systems, detect anomalies, and generate alerts for suspicious activity.
Utilize machine learning to recognize irregularities in data patterns, flagging potential corruption or security threats.
Map data flow from creation to consumption, ensuring transparency in governance and compliance accountability.
Integrating Auditing and Monitoring for Continuous Improvement
Combining audits with real-time monitoring strengthens data governance frameworks by enabling immediate corrective actions. Organizations that establish automated feedback loops between these processes enhance decision-making, reduce compliance risks, and maintain data reliability at scale.
Pro Tip – Implement Automated Compliance Dashboards to visualize audit results and security metrics in real time. This enables leadership and data stewards to quickly identify risks, track policy adherence, and take corrective actions before issues escalate.
Best Practices and Pragmatic Approaches
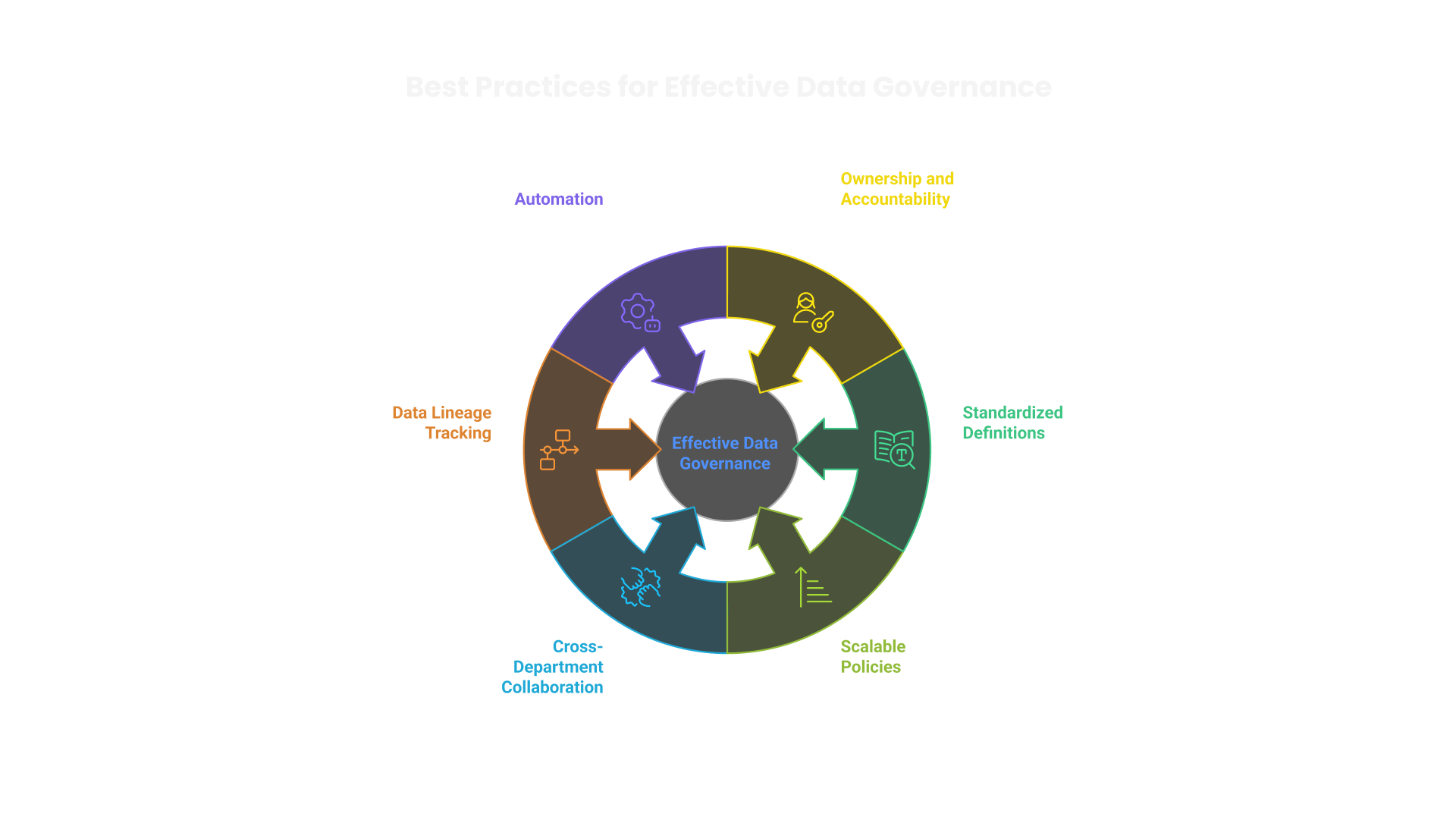
Tackling Common Challenges with Proven Solutions
Data governance initiatives often face resistance, complexity, and compliance hurdles. Addressing these challenges requires precision and a pragmatic approach.
- Overcoming Resistance to Change:
- Managing Data Silos:
- Ensuring Regulatory Compliance:
- Balancing Security with Accessibility:
- Maintaining Governance in Decentralized Environments:
Embed governance culture through executive sponsorship, targeted training programs, and role-based incentives. Practical use cases demonstrate governance value and foster adoption.
Integrate data sources using enterprise-wide data catalogs and API-driven connectivity. Shared access frameworks mitigate fragmentation and improve data accessibility.
Align governance policies with legal mandates using structured control frameworks like GDPR, CCPA, and HIPAA guidelines. Auditable records and real-time monitoring strengthen compliance posture.
Implement role-based access controls (RBAC) and data masking techniques. Restrict sensitive data while maintaining necessary access for analytics and decision-making.
Establish federated governance models where local teams manage data under centralized oversight. This approach preserves agility while ensuring adherence to corporate standards.
Successful governance strategies integrate these best practices with pragmatic execution. Organizations that refine governance frameworks through iterative improvements achieve long-term data integrity, security, and usability.
Data Training and Literacy for Stakeholders
Building Effective Data Training Programs
Organizations that integrate structured data training programs equip stakeholders with the skills needed to handle, interpret, and utilize data effectively. A well-designed program includes multiple components:
- Foundational Data Concepts:
- Regulatory and Compliance Training:
- Data Security Awareness:
- Analytical Skills Development:
- Role-Specific Training:
Covers data types, structures, and governance principles.
Educates teams on data privacy laws such as GDPR, CCPA, and industry-specific regulations.
Teaches best practices for handling sensitive information and mitigating risks.
Enhances the ability to interpret datasets, use visualization tools, and generate reports.
Customized content ensures that executives, analysts, and IT teams receive relevant and actionable insights.
Hands-on workshops, interactive modules, and periodic assessments reinforce learning. E-learning platforms with adaptive learning paths help personalize education based on proficiency levels.
Empowering Stakeholders Through Data Literacy
Data literacy extends beyond basic comprehension; it enables stakeholders to make informed, data-driven decisions. Employees who can confidently assess data accuracy, detect inconsistencies, and extract meaningful insights contribute to better strategic planning.
- Improved Decision-Making:
- Increased Operational Efficiency:
- Enhanced Cross-Team Collaboration:
- Greater Compliance and Risk Mitigation:
Teams base actions on verifiable data rather than assumptions.
Employees spend less time deciphering reports and more time executing strategies.
Shared understanding of data definitions and governance policies reduces miscommunication.
Trained personnel recognize data handling risks and follow procedures that ensure regulatory adherence.
Organizations that prioritize data literacy create a culture where reliable data supports business success. Stakeholders who confidently interpret datasets foster innovation, drive process improvements, and sustain governance standards.
Pro Tip- Leverage Gamification and Real-World Scenarios in data training programs. Interactive challenges, leaderboards, and real-world case studies increase engagement and help employees retain key data governance concepts more effectively.
Driving Enterprise Success with Data Governance
Data governance is not optional. Organizations that systematically manage data governance programs gain competitive advantages, improve compliance, and mitigate risks. A structured approach ensures that data remains accurate, secure, and accessible for decision-making. Without robust governance, enterprises face inefficiencies, security breaches, and regulatory penalties.
Define, Implement, and Review Continuously
Successful data governance requires ongoing commitment. Organizations need to:
- Define clear policies that align with business objectives and regulatory requirements.
- Implement governance frameworks that standardize data management processes.
- Review and adapt policies regularly to keep pace with evolving data landscapes and technologies.
Key Takeaways
- Implementing clear policies, roles, and technologies ensures data integrity, security, and compliance across the organization.
- Encryption, access controls, and continuous vulnerability assessments help safeguard sensitive data from breaches and unauthorized access.
- Managing data from creation to disposal with structured processes ensures relevance, compliance, and efficiency while reducing storage costs.
- Regular audits and real-time monitoring enhance governance effectiveness, ensuring regulatory adherence and proactive risk mitigation.
How effective is your current data governance strategy?
Evaluate existing policies and compare them with industry best practices. Identify gaps, implement necessary improvements, and stay proactive in maintaining compliance and security. Just write to us at info@diggrowth.com and we’ll get back to you.
Ready to get started?
Increase your marketing ROI by 30% with custom dashboards & reports that present a clear picture of marketing effectiveness
Start Free Trial
Experience Premium Marketing Analytics At Budget-Friendly Pricing.

Learn how you can accurately measure return on marketing investment.
How Predictive AI Will Transform Paid Media Strategy in 2026
Paid media isn’t a channel game anymore, it’s...
Read full post postDon’t Let AI Break Your Brand: What Every CMO Should Know
AI isn’t just another marketing tool. It’s changing...
Read full post postFrom Demos to Deployment: Why MCP Is the Foundation of Agentic AI
A quiet revolution is unfolding in AI. And...
Read full post postFAQ's
Data governance is the framework of policies, processes, and roles that ensure data accuracy, security, and compliance. It is essential for maintaining data integrity, enabling informed decision-making, and ensuring compliance with regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, and CCPA.
Organizations can improve data quality by implementing validation rules, standardizing data entry processes, conducting regular data audits, and assigning data stewards to oversee accuracy, completeness, and consistency.
A strong data governance framework includes well-defined policies, clear data ownership and accountability, security measures (such as encryption and access controls), compliance monitoring, and data lifecycle management to ensure long-term data reliability.
Businesses can use role-based access control (RBAC), multi-factor authentication (MFA), and just-in-time (JIT) access to ensure that only authorized users can access sensitive data while maintaining operational efficiency.